Logic
The union of two sets X and Y is equal to the set of elements that are present in set X, in set Y, or in both the sets X and Y. This operation can be represented as;
X ∪ Y = {a: a ∈ X or a ∈ Y}
Let us consider an example, say; set A = {1, 3, 5} and set B = {1, 2, 4} then;
A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
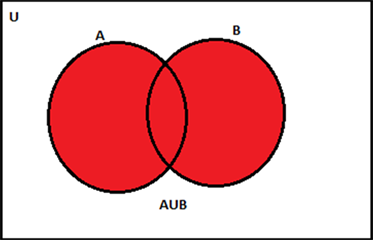
Now, let us learn how can we represent the union of two sets in a Venn diagram.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],b[10],i,c[10],j,k=0,n1,n2;
// taking input set A
printf("Enter number of element of set A\n");
scanf("%d",&n1);
printf("Enter the element of set A \n");
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
// taking input set B
printf("Enter number of element of set B\n");
scanf("%d",&n2);
printf("Enter the element of set B \n");
for(i=0;i<n2;i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
// logic for calculate union
// copy the element of set A in set C
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
// repeted element is not allowed so we check is
any value repeted
for(j=0;j<k;j++)
{
if(c[j]==a[i])
break;
}
if(j==k) //if not repesated then store value in
set c
{
c[k]=a[i];
k++;
}
}
// copy element of set B in set C
for(i=0;i<n2;i++)
{
// check for repeted element
for(j=0;j<k;j++)
{
if(c[j]==b[i])
break;
}
if(j==k) // if element is not repeted then store
in set C
{
c[k]=b[i];
k++;
}
}
// printing of union of set A and set B
printf("Union of set A and B is:-\n");
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
printf("%d ",c[i]);
No comments:
Post a Comment